12 PubMLST Classification
12.1 Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST)
Multi-Locus Sequence Typing (MLST) is a widely-used method for bacterial identification. It is typically more precise and has more resolving power than 16S sequence analysis, but less precise than whole-genome sequence analysis (Maiden et al. (2013)).
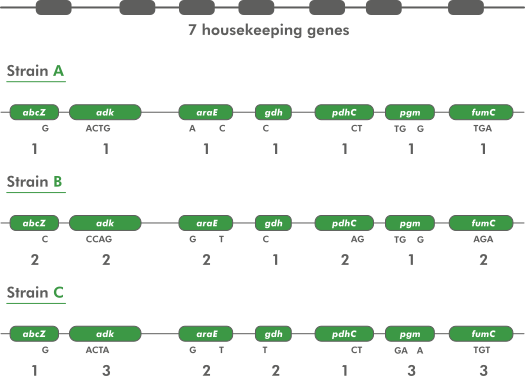
MLST works by defining marker sequences for a taxon (Figure 12.1). These are typically well-conserved (“housekeeping”) genes which very relatively little between organisms in the taxon, but enough to allow discrimination between them. The number of markers varies, but is usually somewhere around seven.
Each marker sequence has many variants (different sequences) within the taxon, and these are known as alleles. Each marker allele is given a unique number (starting at 1 and counting upwards) - its allele number. A single organism’s sequence type (ST) is determined by the list of allele numbers that it contains. Organisms with the same sequence type are considered to be part of the same group.
12.2 MLST Classification with Galaxy
The PubMLST.org website hosts a collection of open-access, curated databases that integrate population sequence data with provenance and phenotype information for over 130 different microbial species and genera. These databases are curated and maintained by volunteers and made available freely for use by anyone. They are available in Galaxy.
The MLST software is made available in Galaxy for querying bacterial sequences against the pubMLST databases. To do this:
- Navigate to the
MLSTtool in theToolssidebar - Select the
ERR531380assembly as theinput_files - Click on
Run Tool - Click on the
Eyeicon to see the result
MLST tool to classify your isolate
What is the sequence type (ST) of your isolate as reported by Galaxy MLST?
✗paeruginosa
✓395
✗6, 5, 1, 1, 1, 12, 1
Check the Help section of the MLST tool for a description of the output format.
12.3 Classification at pubMLST
The PubMLST.org website also provides its own search and classification tools. Some of these are genus or species specific, running queries against databases focused on classification of a particular group of organisms, but they also provide a much braoder classification scheme with a much larger number of markers that you may have met in a BM329 workshop.
Here, you will use PubMLST’s Pseudomonas aeruginosa-specific database to identify your assembled isolate.
- In a new tab of your browser open the PubMLST website
- Click on
Organisms - Navigate to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and click on
Typing - Under
Query a sequenceclick onSingle sequence - Select the
ERR531380assembly as input - Click on
SUBMIT
The pubMLST classification may take a couple of minutes.
PubMLST to classify your isolate
- Does
PubMLSTassign the same sequence type (ST) to your isolate asGalaxy’sMLSTtool did?
12.4 Next Steps
Now you have assembled and classified your isolate, you can use some additional data prepared by your helpful colleague to reconstruct a phylogenetic tree for isolates obtained from the burns ward.