12 Find Sequence Variants
snippy is a sequence variant finding pipeline, designed for haploid genomes such as prokaryotes and viruses.
As with most kinds of bioinformatics data, there is a data format designed specifically to capture the important elements of the data, and snippy outputs its results in this format.
ImportantGood practice
When reporting how you identified variants for your manuscript or dissertation, you should always state:
- The software tool you used, with its version number and a citation of the paper describing it (if available; provide a URL to the software if there is no paper)
- The parameters used when running the tool (if default parameters were used, state this)
12.1 Using snippy
- Navigate to the
snippytool - Select
snippy - Select
Use a genome from history and build indexfromWill you select a reference genome… - Choose the
SARS_AY278741.gbkfile inUse the following dataset as the reference sequence - Select
Paired end readsunderSingle or Paired-end reads - Choose the cleaned post-
trimmomatic(R1 paired)data for the forward reads - Choose the cleaned post-
trimmomatic(R2 paired)data for the reverse reads - Click
Run Tool
NoteVideo: Identifying sequence variants using
snippy
Caution
snippy can take a few minutes to run to completion.
12.2 snippy Output
snippy provides output in .vcf format, which is designed to be processed by bioinformatics software and is not the most understandable form for humans. To see the snippy output in a more human-readable form, click on the eye icon for the snps table output (Figure 12.1).
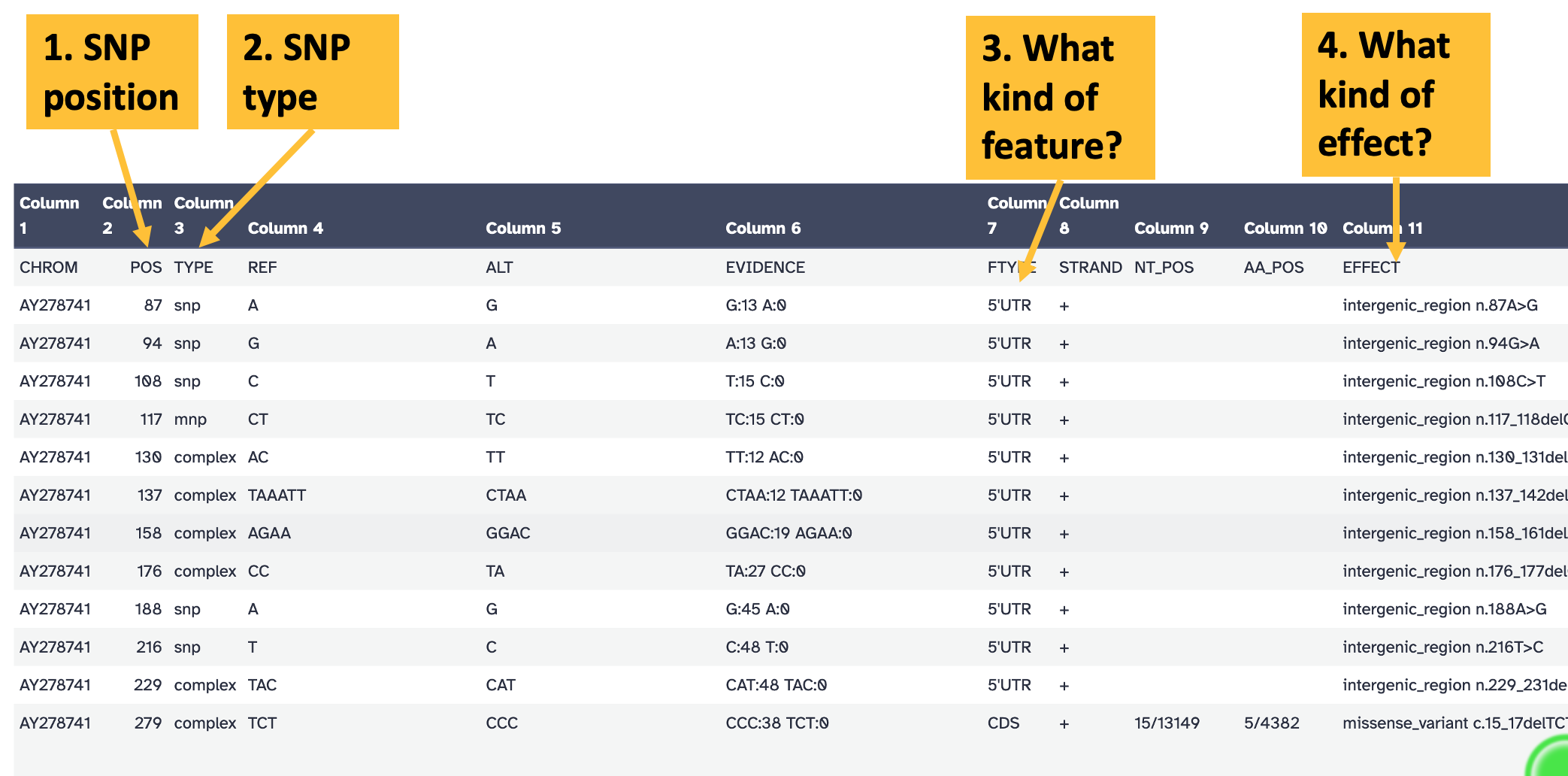
snippy snps table output. Key columns in the output are: column 2, indicating the position of the variant; column 3, indicating the variant type; column 7, indicating the feature affected by the variant; and column 11, summarising the effect of the variation
NoteVideo: Inspecting
snippy output
TipQuestions
- Can you find these SNPs manually using JBrowse?
- Are any SNPs different or inconsistent between the
JBrowseandsnippyoutputs?