2 Register An Account with Galaxy
2.1 Introduction
In this workshop you will be working on Galaxy, an open source scientific workflow and data integration platform (Galaxy Community (2024)). Galaxy is a framework for performing reproducible computational biology and bioinformatics, democratising the field so that scientists with no programming or other computing experience can still carry out bioinformatic analyses on their own data, in their web browser.
The Galaxy software is open source and can be downloaded and installed freely on any computer that it can run on. Each such installation is called a Galaxy instance. The Galaxy instance that you will be working on is the EU Galaxy instance at https://usegalaxy.eu/. This is the largest Galaxy instance in Europe and gives access to over 2500 scientific tools. It is free to use, and is maintained by the Galaxy team at Freiburg.
There are many other Galaxy instances, some private, and some public and free for anyone to use, such as:
- https://usegalaxy.org/: The Galaxy Project public server, supporting biomedical research.
- https://galaxyproject.org/use/usegalaxy-fr/: A general-purpose Galaxy server, based in France
- https://galaxyproject.org/use/usegalaxy-au/: The Australian UseGalaxy server
Galaxy can be thought of as a library of bioinformatics tools and, just as different libraries may contain differing collections of books, each Galaxy instance may make available different sets of tools, or different versions of similar tools. As a result some analyses may be possible on one Galaxy instance, but not another.
When you use Galaxy it is important to be clear when writing up your analysis methods to be clear about which Galaxy instance is used, and which version of each tool was used in the analysis.
2.1.1 Workflows
The key concept in Galaxy is the workflow. A workflow is a series, or chain, of analysis steps that takes some input data (one or more files or datasets) through a series of actions, to generate one or more result files. Typically, the output of one step will serve as the input to the next step, but more complicated branching workflows can also be created (Figure 2.1).
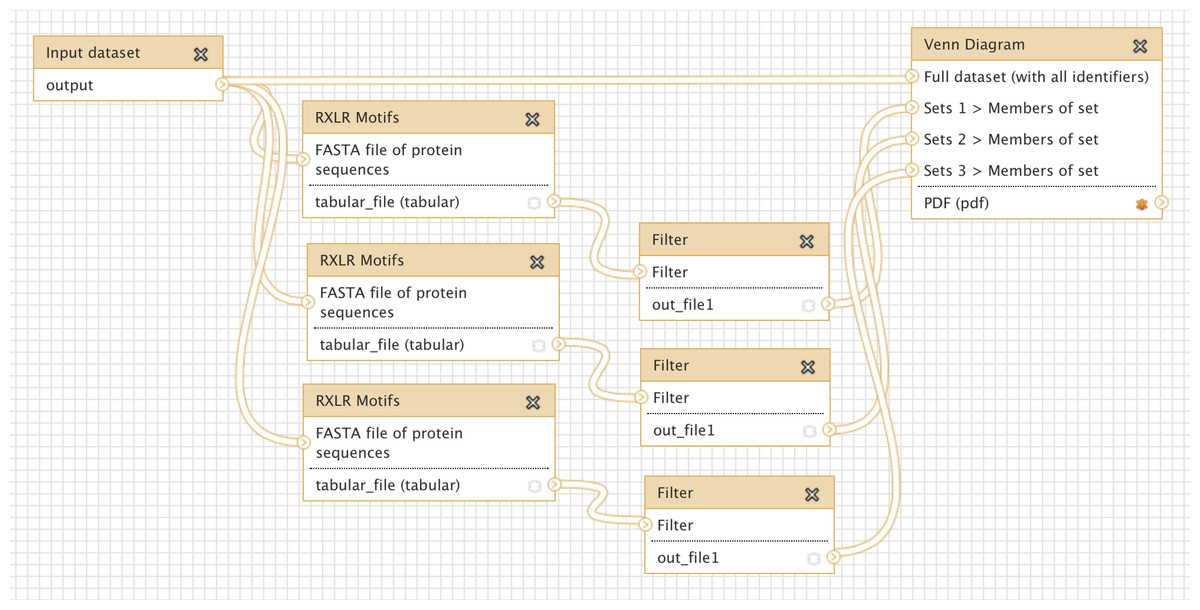
RXLR Motifs) with three different settings, and compares the results using a Venn diagram (reproduced from Cock et al. (2013)). The workflow runs from left to right. A single Input dataset is fed into the RXLR Motifs tool three times, applying a different method each time. Each run of the RXLR Motifs tool generates a different set of output sequences, which are passed as input to the Filter tool. The output from all three runs of the Filter tool is passed to the Venn Diagram tool, along with the original input dataset, to generate a Venn Diagram
Using Galaxy, you will build up a powerful bioinformatic analysis workflow to analyse your data, step-by-step, using a web browser. Galaxy allows you to save and share your workflows, to encourage reuse and reproducibility.
2.2 Registering with Galaxy
usegalaxy.eu
The first action you should take in this workshop, if you do not already have an account at https://usegalaxy.eu/, is to create an account at https://usegalaxy.eu/.
- Go to the Galaxy login/registration page
- If you have a
usegalaxy.euaccount already, then log in using your details and move on to the workshop proper. - If you do not already have a
usegalaxy.euaccount, then click on theRegister herelink. - Enter your university email address in the
Email addressfield. - Choose a secure password and enter it into the
PasswordandConfirm passwordfields. - Choose a public name to show (other people will be able to see this) and enter it in the
Public namefield. - Click on the
Createbutton.
You will receive a validation email at the account you register with. You must confirm your email to proceed.